How Does a Stamping Press Work?

A stamping press is a machine used in manufacturing processes to shape or form metal sheets or other materials into desired shapes or parts.
A stamping press is a machine used in manufacturing processes to shape or form metal sheets or other materials into desired shapes or parts. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and appliances. In this explanation, I will provide an overview of how a typical stamping press works.
Basic Components:
A stamping press consists of several essential components, including the following:
Frame: The frame provides the structure and support for the press. It is typically made of heavy-duty steel and is designed to withstand the forces generated during the stamping process.
Bed: The bed is a large, flat surface located at the bottom of the press. It provides a stable platform for the material being worked on.
Ram: The ram is the moving component of the press. It is connected to the upper part of the frame and moves up and down to apply force on the material.
Die Set: The die set is a specialized tooling system that consists of upper and lower dies. The upper die is attached to the ram, while the lower die is mounted on the bed. The dies have cavities or contours that define the shape of the final part.
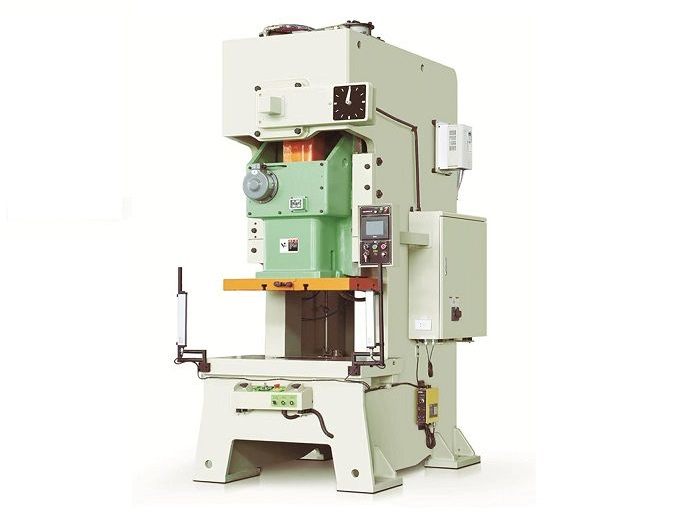
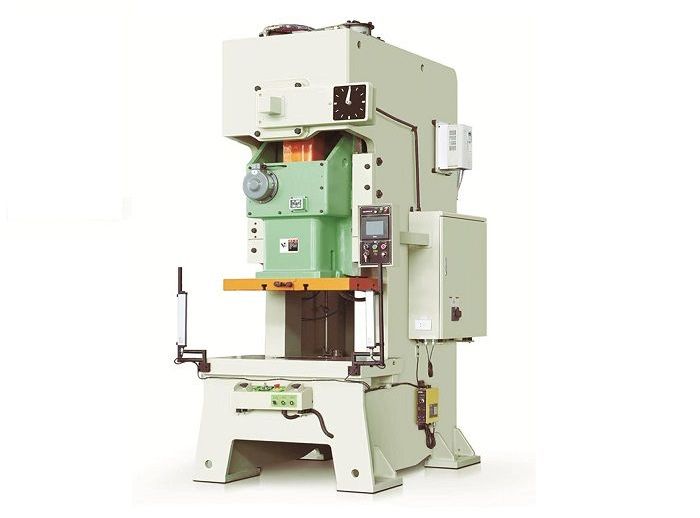
Single Crank C Frame Press Machine
Operation:
The operation of a stamping press involves a series of steps:
Material Preparation: The process begins with preparing the material, which is usually a metal sheet or coil. The material may undergo cleaning, lubrication, or other treatments to improve its workability and reduce friction.
Feeding: The material is then fed into the stamping press. This can be done manually or through an automated feeding system. The material is guided between the upper and lower dies, ensuring proper alignment.
Die Closure: Once the material is in place, the ram moves downward, causing the upper die to close onto the lower die. This creates a cavity that matches the desired shape of the final part.
Material Deformation: As the dies close, the material is subjected to high pressure and force. This causes the material to deform and take the shape of the die cavity. The amount of force applied depends on the material's properties and the complexity of the part being formed.
Ejection: After the material has been formed, the dies open, and the ram moves back up. At this stage, an ejection system may be employed to remove the part from the dies. This can involve the use of ejector pins, air jets, or other mechanisms.
H Frame High Speed Press Machine
Types of Stamping Presses:
Stamping presses come in various types, each suited for different applications:
Mechanical Press: A mechanical press uses a flywheel and a clutch mechanism to generate the necessary force. It is suitable for medium to heavy-duty stamping operations and offers high precision and repeatability.
Hydraulic Press: A hydraulic press uses hydraulic cylinders to generate force. It provides a greater degree of control over the force and speed, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Servo Press: A servo press combines the advantages of mechanical and hydraulic presses. It uses a servo motor for precise control of force and speed. This type of press is often preferred for complex forming operations and fine-tolerance parts.
Transfer Press: A transfer press is used for high-volume production and is capable of transferring the material between multiple stations. It allows for simultaneous processing of different operations, such as bending, cutting, and forming.
In conclusion, a stamping press is a versatile machine used in metalworking industries to shape materials into desired parts. By applying force and pressure, it deforms the material using a die set, resulting in the creation of various components. The specific type of press used depends on the requirements of the application, with mechanical, hydraulic, servo, and transfer presses being commonly employed.
For more information, please contact us. We will provide professional answers.